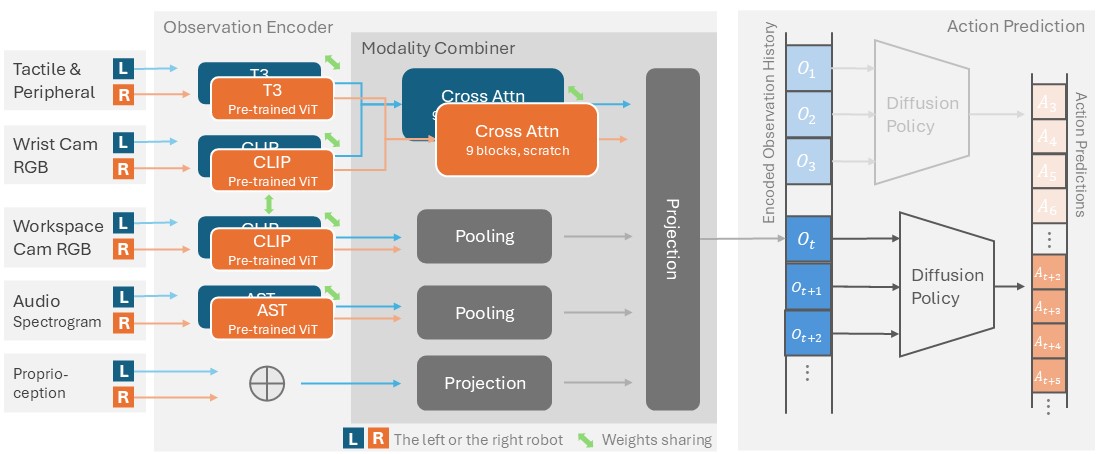
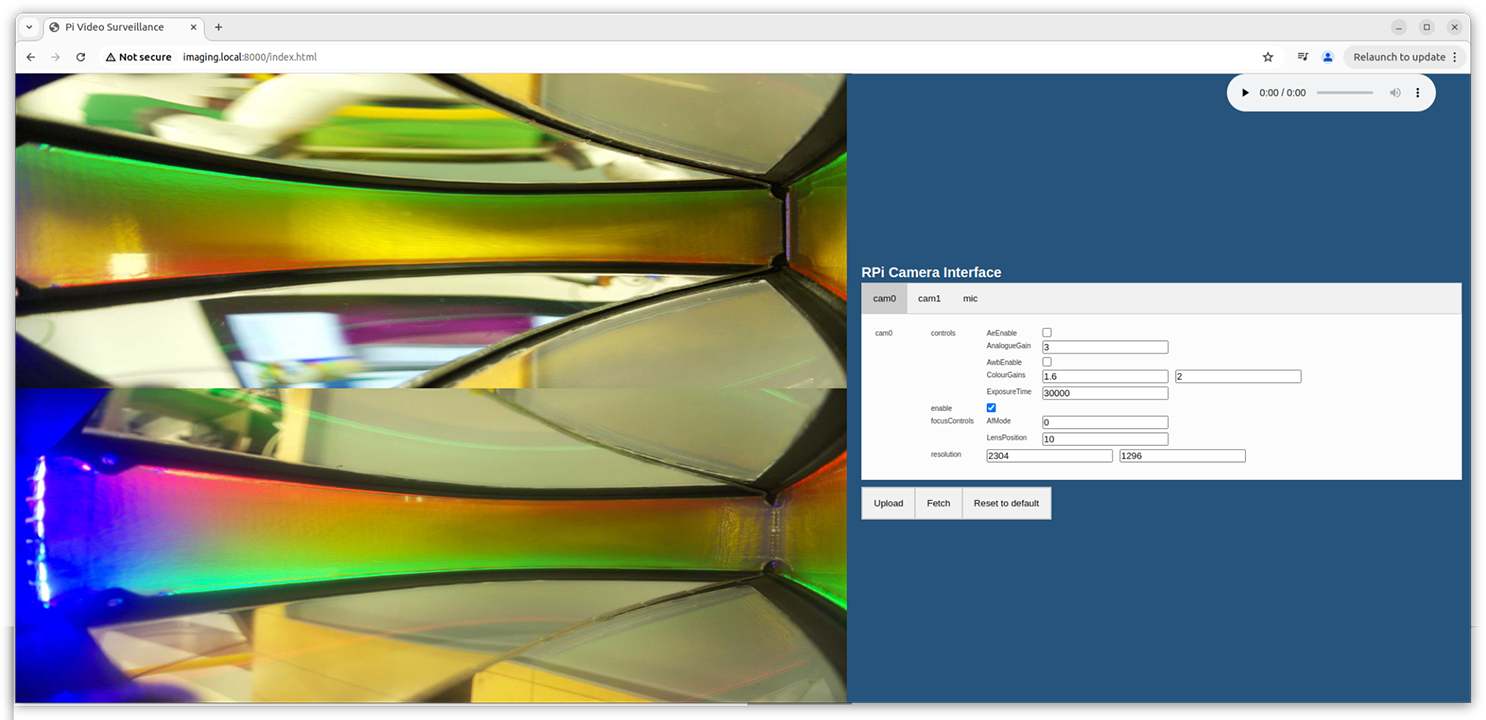
3 modalities in 1 cable
with one camera and one contact microphone,
Tactile sensing see the detailed texture just like GelSight, DIGIT, DenseTact etc.
Peripheral vision see exactly what's grasped and the surroundings
Acoustic sensing hear the making and breaking of contacts
One repurposed HDMI cable provides power input and data output. On the other side all data is processed by a Raspberry Pi with an easy-to-use interface for real-time streaming or saving.

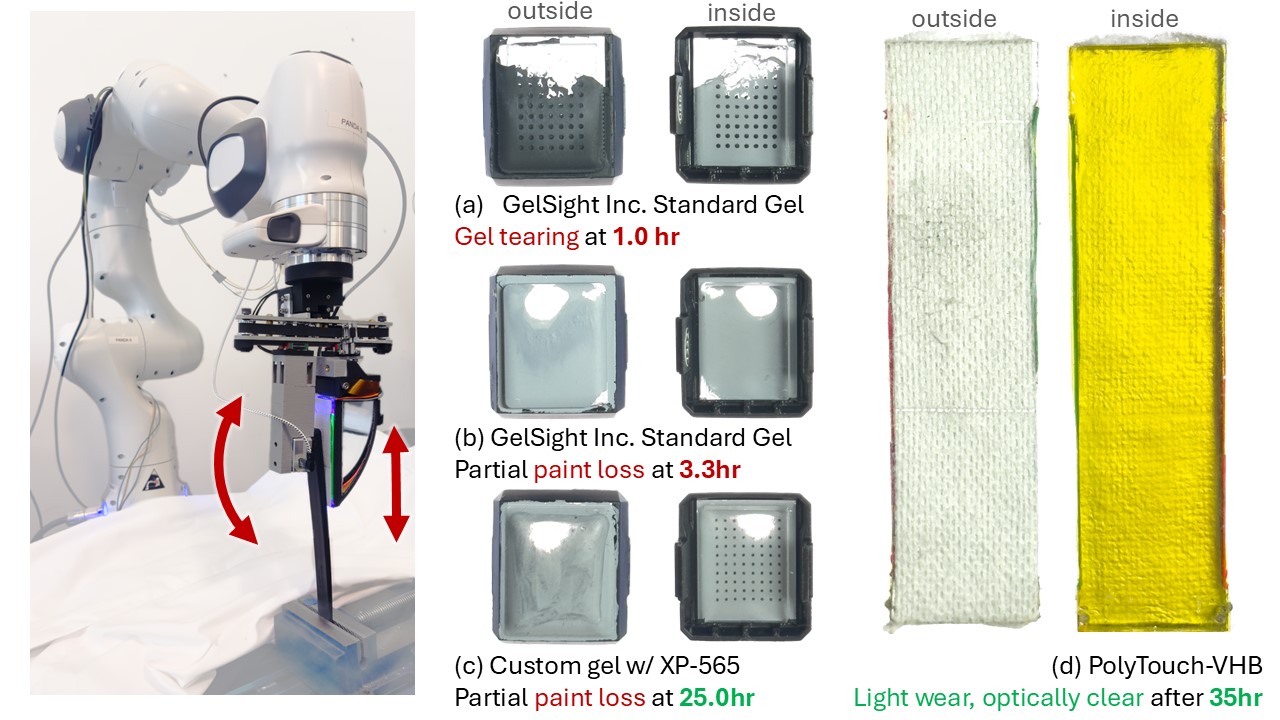
At least 20x lifespan
GelSight Inc. sensors last only 1-3 hrs in our durability test which emulates a continous tool-using environment.
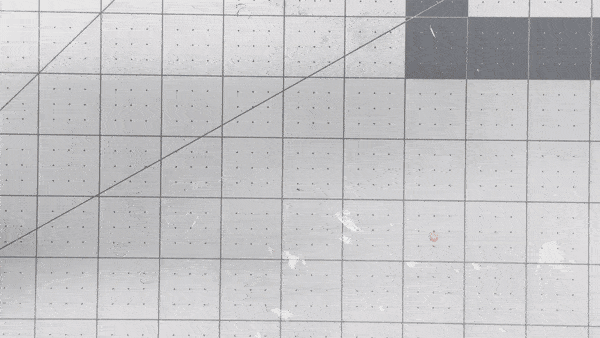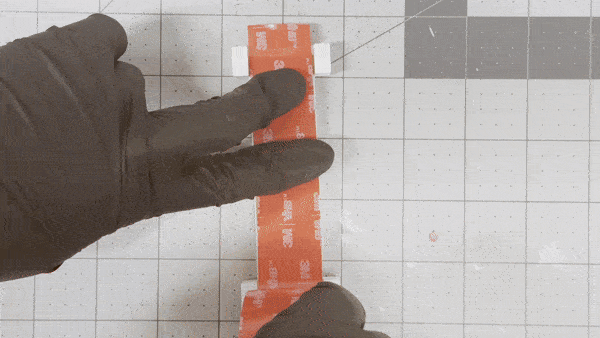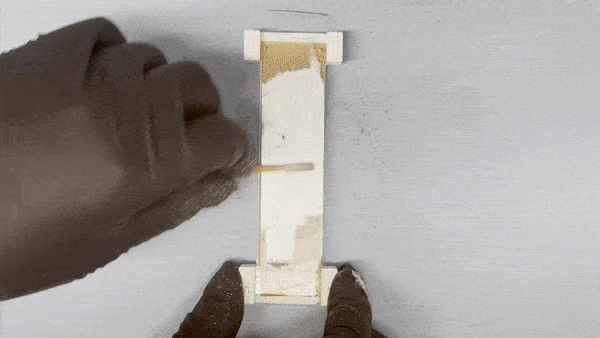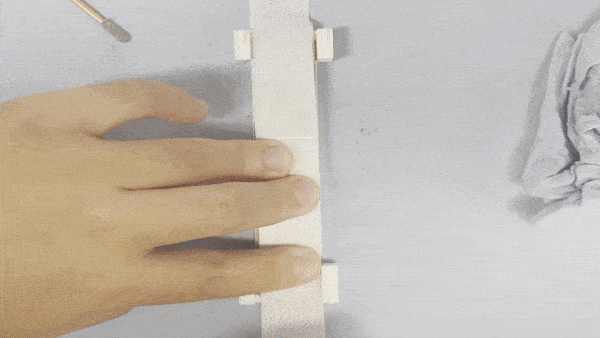
This lifespan increase was achieved thanks to a novel yet very accessible elastomer (3M VHB tape) and protective layer (3M Nexcare), which eliminates delamination and reduces wear and tear.

Abstract
Achieving robust dexterous manipulation in unstructured domestic environments remains a significant challenge in robotics. Even with state-of-the-art robot learning methods, haptic-oblivious control strategies (i.e. those relying only on external vision and/or proprioception) often fall short due to occlusions, visual complexities, and the need for precise contact interaction control. To address these limitations, we introduce
More Details
Check more details about
@misc{zhao2025polytouchrobustmultimodaltactile,
title={PolyTouch: A Robust Multi-Modal Tactile Sensor for Contact-rich Manipulation Using Tactile-Diffusion Policies},
author={Jialiang Zhao and Naveen Kuppuswamy and Siyuan Feng and Benjamin Burchfiel and Edward Adelson},
year={2025},
eprint={2504.19341},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.RO},
url={https://arxiv.org/abs/2504.19341},
}